


A quasistatic parameter (hereafter referred to as qint) is an constant integer used by the program in such a way that the initialization value of the constant integer may be selected from the any of the N values specified at the definition of the parameter, without changing the functional behavior of the program; it is similar to the notion of dynamically-valued constants discussed in [].
A qinfluence statement is used to indicate to the clever compiler what parts of the program should have their performance associated with a given qint parameter.
Again, I present examples to demonstrate the intended semantics of the construct.
The code in Figure  illustrates that
when matrices to be multiplied are too large to work on at once, they
can be divided up into sub-matrices and multiplied, and then the
results composed to get the final answer; the possible values for
blocking size are 1024, 2048, and 4096 in this case.
Figure
illustrates that
when matrices to be multiplied are too large to work on at once, they
can be divided up into sub-matrices and multiplied, and then the
results composed to get the final answer; the possible values for
blocking size are 1024, 2048, and 4096 in this case.
Figure  is semantically equivalent
to Figure
is semantically equivalent
to Figure 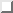 , and demonstrates the use
of the `` :'' notation for specifying ranges of values. Exactly
which blocking size results in the best performance depends heavily on
both static machine characteristics
, and demonstrates the use
of the `` :'' notation for specifying ranges of values. Exactly
which blocking size results in the best performance depends heavily on
both static machine characteristics like cache size/associativity, and dynamic characteristics like cache
competition introduced by other processes under multitasking operating
systems.
like cache size/associativity, and dynamic characteristics like cache
competition introduced by other processes under multitasking operating
systems.
The effect of using a qint parameter can be achieved by writing
N pieces of alternative code (in each of which the quasistatic
parameter symbol is substituted with a literal from the parameter's
set of possible values) chained together in a qif statement;
however, the net effect achieved is desired commonly enough to merit
special treatment. Furthermore, encoding the alternatives using a
qint parameter instead of N quasistatic variables in long
qif statements potentially allows a clever compiler to more
efficiently search the version space by guessing that to a first
approximation, performance of a particular version of a program can be
estimated by interpolation on the differences in qint parameter
values between it and program versions which have already been tried.
E.g., if the program versions 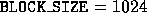 and
and 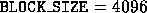 have already been tried, then a clever compiler
might guess that to a first approximation, performance of the
have already been tried, then a clever compiler
might guess that to a first approximation, performance of the
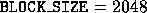 version of the program falls somewhere between
the performance of those two versions.
version of the program falls somewhere between
the performance of those two versions.
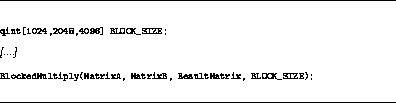
Figure: qint example: matrix multiplication.
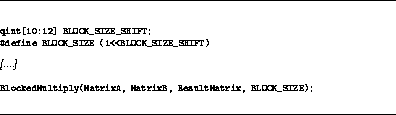
Figure: qint example (alternative syntax).
As another example, in Figure  , the
programmer has access to remote computation services but is not
certain whether their performance is good compared to just performing
computation locally --- the servers are likely to be shared with other
users, for example, so if other users are often making heavy demands,
the servers will be relatively unresponsive. Using qint
parameters allows dynamically balancing between client and server
processing.
, the
programmer has access to remote computation services but is not
certain whether their performance is good compared to just performing
computation locally --- the servers are likely to be shared with other
users, for example, so if other users are often making heavy demands,
the servers will be relatively unresponsive. Using qint
parameters allows dynamically balancing between client and server
processing.

Figure: qint example: load splitting.
The access scope of a qint parameter should be the same as that of a C integer variable definition appearing in the same textual position in the source code file. By default, if there are no qinfluence statements in the program which reference a qint, for profiling feedback purposes, the entire part of the program where the qint is lexically visible is assumed to be influenced by which particular value which the clever compiler assigns to the qint. Note that this default can be simultaneously both too broad and too narrow in scope. The value of a qint parameter may not affect program performance for all the code within its lexical scope, and including more code than necessary will tend to swamp out any performance effects of changing the value of the qint parameter; conversely, mutations allow the qint value to influence code performance outside its lexical scope.
Where the programmer believes this default would be substantially
inaccurate, the qinfluence construct allows him or her to
indicate explicitly what parts of the code he or she believes will
have their performance influenced.
Figure  demonstrates usage of the
qinfluence construct; the programmer has provided more information to
the compiler than in Figure
demonstrates usage of the
qinfluence construct; the programmer has provided more information to
the compiler than in Figure  . Note
that no qinfluence(USE_REMOTE_COMPUTATION_SERVER_LIMIT)
statement is necessary in this example since the entire lexical scope
of that qint parameter is the correct scope for the clever
compiler to be looking at profiling feedback.
. Note
that no qinfluence(USE_REMOTE_COMPUTATION_SERVER_LIMIT)
statement is necessary in this example since the entire lexical scope
of that qint parameter is the correct scope for the clever
compiler to be looking at profiling feedback.
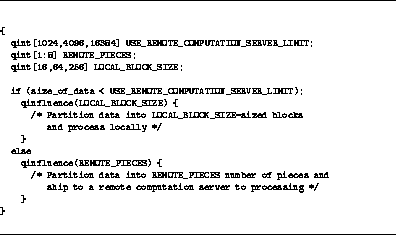
Figure: qint example ( qinfluence syntax).